Preventing Hypoglycemia in Endurance Athletes
Hypoglycemia, a condition characterized by abnormally low blood sugar levels, can severely impact athletes, particularly endurance athletes. This is especially true during prolonged physical activity when glucose reserves become depleted. It is crucial for athletes to recognize the warning signs of hypoglycemia, including dizziness, confusion, shaking, and extreme fatigue. Awareness of these symptoms can help in taking prompt action to address the issue before it leads to severe consequences. Educating athletes about their physiological responses during endurance activities is vital. They must be familiar with what hypoglycemia feels like to avoid potential dangers. Additionally, understanding how nutrition affects performance is crucial. A balanced intake of carbohydrates prior to exercise can help maintain stable blood sugar levels. Monitoring carbohydrate intake during endurance events is equally important to prevent sudden drops in glucose levels. Athletes should make conscious choices about their pre-competition meals and snacks. Building a strategy for nutrition can contribute to fewer complications related to hypoglycemia. Finally, it’s important to maintain open communication with teammates and coaches regarding energy levels and how to manage them effectively.
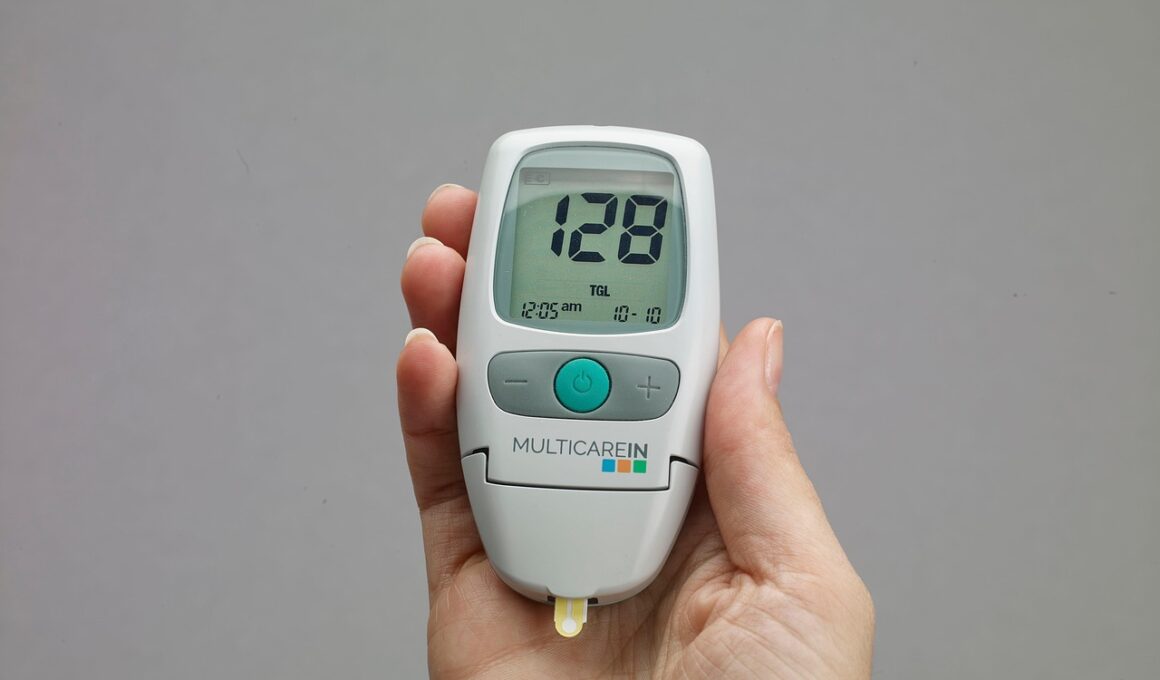
To further prevent hypoglycemia during training and competition, athletes should incorporate a structured nutrition plan. A well-crafted nutrition strategy can greatly reduce the risk of experiencing low blood sugar. Consulting with a sports nutritionist can provide tailored advice on carbohydrate loading, hydration, and the timing of meals. It’s advisable to consume easily digestible carbohydrates during endurance events. Options include energy gels, chews, or sports drinks that can quickly raise blood sugar levels without causing gastrointestinal distress. Athletes should test different products during training to find what works best for their body. Similarly, frequent monitoring of blood glucose levels, when applicable, can guide athletes in making informed decisions before and during their activities. Having a glucose monitoring device on hand during competitions may reduce risks associated with hypoglycemia. Additionally, athletes should practice their nutrition strategies specifically for race day. Understanding how different foods impact energy levels can prepare athletes for high-intensity efforts. In summary, effective management of hypoglycemia centers around meticulous planning of nutrition, listening to the body, and having emergency solutions accessible at all times.
Understanding the Causes of Hypoglycemia
Recognizing the possible causes of hypoglycemia is fundamental for athletes aiming to prevent this condition. Numerous factors can lead to low blood sugar levels. For endurance athletes, one significant cause is prolonged exercise without proper nutrition. During extended activities, glycogen stores become depleted, resulting in insufficient energy for bodily functions and performance. Athletes may sometimes underestimate the importance of refueling. In addition to exercise, the timing and composition of meals before an event contribute significantly to energy levels. Consuming high-fiber or high-fat foods can slow digestion, leading to a delayed release of glucose. This results in potential energy dips during performance. Moreover, medical conditions such as diabetes can make an athlete more susceptible to hypoglycemia. If athletes use insulin or medications to manage these conditions, they must be incredibly vigilant. Awareness of these potential risks allows athletes to formulate a proactive strategy. It focuses on pre-competition fueling and maintaining energy levels throughout competition. Understanding these causes creates a comprehensive framework for nutrition and hydration management tailored specifically to endurance sports, ultimately minimizing the risk of hypoglycemia during rigorous training or competitions.
Hydration plays a crucial role in maintaining blood sugar levels and preventing hypoglycemia during endurance events. Dehydration can exacerbate issues related to low glucose, as it may influence the body’s ability to metabolize food efficiently. Athletes should target maintaining hydration before, during, and after exercise. Consuming fluids rich in electrolytes can offer additional benefits beyond mere hydration. They can help replace what is lost through sweat, allowing better physiological performance. Sports drinks are commonly used for this purpose, balancing carbohydrates and hydration effectively. Maintaining good hydration is essential to sustaining energy levels. Athletes are encouraged to hydrate regularly, irrespective of whether they feel thirsty. Regular fluid intake can help prevent sudden drops in blood sugar during workouts or competitions. Keeping track of fluid intake can help athletes ensure they do not fall behind. Moreover, establishing a hydration schedule during training sessions can promote consistency on race day. This awareness and preparation can play a substantial role in managing glucose levels effectively, thus reducing the risk of hypoglycemia during high-endurance activities.
Signs and Symptoms of Hypoglycemia
It’s vital for athletes to familiarize themselves with the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia, enabling timely interventions. Common symptoms include intense hunger, weakness, trembling, irritability, and confusion. As blood sugar continues to drop, more severe symptoms can emerge, such as increased sweating, dizziness, and even loss of consciousness. Athletes experiencing these symptoms must act quickly. It’s important not to ignore mild symptoms, as they often escalate rapidly. Consuming fast-acting carbohydrates can act as a first response to counteract hypoglycemia effectively. Options include glucose tablets, sugary beverages, or fruit juices. They elevate glucose levels quickly. After initial relief, incorporating a source of longer-lasting carbohydrates is advisable. This helps stabilize blood sugar over time. Athletes should always carry a reliable source of quick carbohydrates, particularly during long events. Sharing knowledge about symptoms of hypoglycemia within the athlete community also contributes to collective safety. Teammates and coaches informed about these symptoms can assist a struggling athlete in seeking help. In summary, recognizing hypoglycemia can be crucial for ensuring the athlete’s safety and performance during both training and competitions.
In addition to recognizing symptoms, having a management plan for hypoglycemia is vital for athletes. Alongside quick carbohydrate sources, athletes should establish a protocol to follow if symptoms arise. This could entail identifying safe spaces to sit and recover or having trusted teammates ready to assist. Additionally, an emergency contact plan should be in place, enabling communication with health professionals if necessary. Athletes should prioritize discussing their hypoglycemia concerns with coaches or trainers. Open communication ensures that all relevant parties understand the athlete’s condition and management strategies. Moreover, training sessions should include discussions around managing energy levels and recognizing symptoms among peers. Such practices foster a supportive environment for athletes. Athletes may also benefit from educational resources on hypoglycemia. Attending workshops that discuss sports nutrition specialized for their needs can empower them. This educational approach creates more knowledgeable athletes who can engage in their nutrition while also preserving their health. Engaging coaches and support staff in discussions may prove beneficial. This comprehensive approach to hypoglycemia ensures a safer and more enjoyable endurance experience for athletes working to achieve their personal best.
Conclusion: Steps to Combat Hypoglycemia
In conclusion, preventing hypoglycemia in endurance athletes is a complex yet achievable goal. Athletes must focus on understanding their bodies in relation to nutrition, hydration, and awareness of symptoms. Establishing a proactive strategy by creating individualized nutrition plans tailored to specific needs and incorporating regular refueling practices can effectively minimize risks. Additionally, staying hydrated can enhance efforts to maintain stable blood sugar levels during prolonged physical activity. Athletes need to recognize signs of hypoglycemia and have a management plan ready to execute. This includes knowing what quick carbohydrates to consume and when to seek help. Furthermore, engaging in open communication with trainers and peers fosters a supportive network that prioritizes health. Regular collaboration with nutritionists and healthcare providers can lead to ongoing improvement in strategies for managing blood sugar levels. Continued education about the implications of hypoglycemia allows athletes to take charge of their health effectively. In summation, the collective commitment to knowledge, planning, and communication enhances the well-being of endurance athletes concerning managing hypoglycemia during their rigorous training and competition cycles.
Knowledge of these preventative measures not only enhances athletic performance but also promotes the lifelong health of endurance athletes.