Recognizing Hypoglycemia Symptoms in High-Intensity Sports
Hypoglycemia, also known as low blood sugar, can be particularly dangerous for athletes engaged in high-intensity sports. This condition arises when the glucose levels in the blood drop below normal. Athletes often require substantial quantities of fast-acting energy, and a dip in blood sugar can hinder performance. Common symptoms of hypoglycemia include dizziness, weakness, confusion, sweating, irritability, and even fainting. The athlete might notice feelings of fatigue and increased hunger. For some, hypoglycemia can lead to severe complications if not promptly addressed. Recognizing these symptoms early is critical to ensure the athlete’s safety. Furthermore, treating hypoglycemia effectively requires understanding the immediate need for glucose or sugar intake. Athletes should be educated on their body’s response during training or competition. Education can help in developing a plan that includes hydration and proper nutrition, focusing on the intake of carbohydrates before, during, and after activity. Nutritional strategies could include consuming energy gels, fruits, or flavored drinks. Understanding these essential factors is key for optimal performance for athletes in high-performance environments.
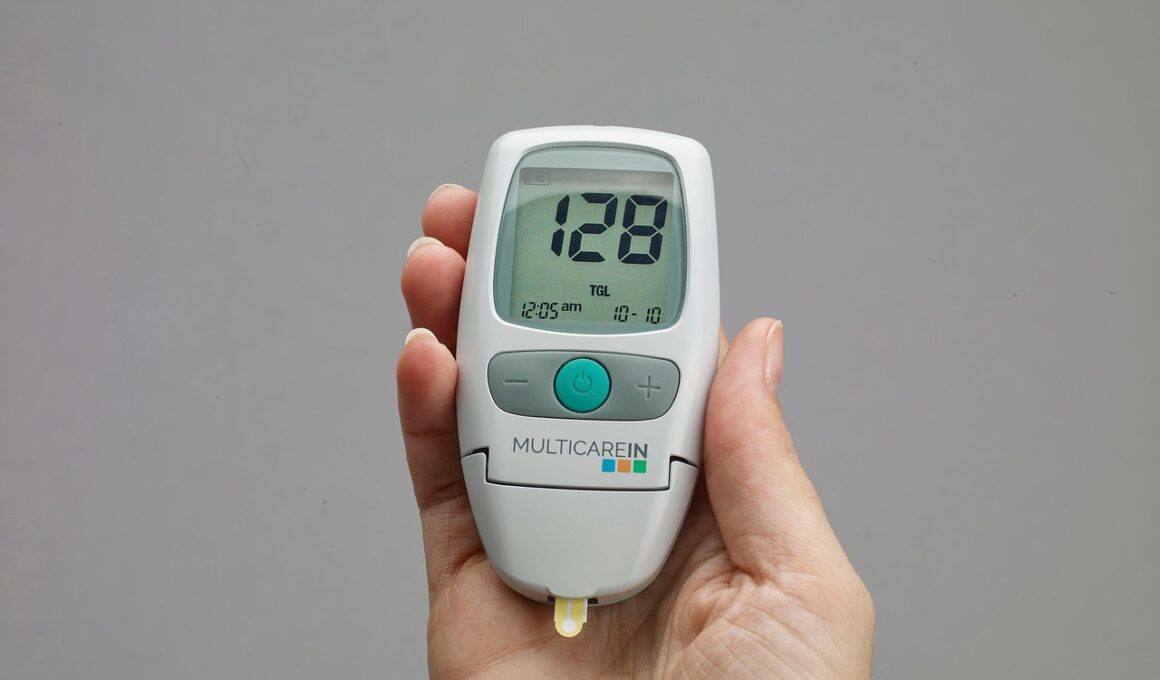
Monitoring blood glucose levels can also aid in recognizing hypoglycemia. Regular testing and awareness of an athlete’s specific dietary needs can reduce risks associated with intense training. Athletes with diabetes should take special precautions, ensuring they have an adequate supply of fast-acting carbohydrates available during training sessions. This preparation can happen before a game or race. Encouraging athletes to maintain a balanced nutrition plan ensures they have the right amount of energy for their activities. When athletes prepare themselves with knowledge, snacks, and supplemental options, the chance of experiencing hypoglycemia diminishes. Coaches and trainers must be proactive in educating their athletes about the signs and prevention strategies. During competitions, having quick-access resources, like glucose tablets or sugary drinks, can be helpful. Regular hydration is also essential in managing energy levels during exertion. Mental awareness of body signals can enhance an athlete’s performance and reduce the likelihood of adverse effects. Enhancing communication between athletes, coaches, and medical professionals fosters a supportive environment. Maintaining open dialogue about dietary management, physical health, and performance can substantially enhance safety and well-being overall.
Recognizing Symptoms of Low Blood Sugar
Recognizing symptoms of hypoglycemia is essential for timely response and recovery. Athletes should prioritize education to self-manage their condition during training or competition. Common symptoms include shakiness, blurred vision, rapid heartbeat, anxiety, and confusion. Each individual may experience symptoms differently; hence, awareness is pivotal. Advanced strategies can help identify these conditions. For example, some athletes may benefit from monitoring their heart rate and perceived exertion as they train. Athletes can also keep a journal of their blood glucose levels, thoughts, and feelings during physical exertion. This approach helps identify possible patterns associated with low blood sugar. Learning individualized indicators can lead to better self-management practices. Encouraging periodic check-ins about energy levels with a trusted coach can strengthen accountability. Coaches can reinforce the importance of stability and consistency in an athlete’s nutrition plan. It’s crucial to understand proper pre-game and pre-training meals to sustain energy levels throughout the activity. Sweet snacks that are easy to digest, like granola bars or banana slices, can be incredibly effective in maintaining blood sugar levels. These small adjustments may dramatically improve an athlete’s readiness for their performance.
When working out, proper hydration also plays a significant role in managing blood sugar levels. Dehydration can lead to suboptimal performance and increased risk of hypoglycemia. Having a personalized drink strategy that defines what and when to consume fluids can contribute significantly to energy maintenance. This should include electrolytes to expedite recovery and improve overall hydration. Athletes involved in intense training should tailor their meals around carbohydrates and proteins, optimizing their body’s use of glucose. Finding the right balance requires collaboration with nutritionists or dietitians who specialize in sports nutrition. These professionals can help craft tailored meal plans that meet the individual requirements of athletes based on their specific sport. Prioritizing macronutrient intake, particularly carbohydrates before and after workouts, promotes recovery and sustained performance. Knowing what to eat and when can prevent the onset of hypoglycemia during intense activities. Furthermore, athletes should familiarize themselves with how different foods affect their energy levels. The interaction between their training rate and eating habits is crucial for performance. By sticking to a well-structured plan, athletes can focus better on their performance rather than managing lows.
Managing Hypoglycemia in Training
A proactive approach involves understanding and preparing for hypoglycemia during training sessions. Athletes should carry glucose tablets, energy gels, or candy for quick access to sugar if they experience symptoms. During long or intense training sessions, athletes must note their energy levels, especially during high-impact activities. Keeping a journal of food choices and energy levels during various training phases helps identify what may lead to lows. This process encourages athletes to learn their body’s signs, improving self-management and long-term performance. Coaches and trainers should ensure that athletes have opportunities to practice self-checks during training as well. Encouraging open communication can significantly enhance an athlete’s ability to respond effectively to low blood sugar. Establishing action plans that outline specific steps athletes should take can provide additional support. For instance, if symptoms arise, the athlete should have a clear route to recover quickly and be topped up on energy. Emphasizing consistent nutrition and hydration during practice can minimize energy crashes. Working closely with medical professionals creates a solid support system while facilitating a safe training environment.
After training, it is crucial to refuel the body adequately to stabilize blood sugar levels. Recovery meals containing carbohydrates and proteins help restore energy supplies. Ideally, athletes should eat within thirty minutes after intense training. This approach expedites muscle repair and replenishes glycogen. Supplementing post-workout with protein shakes or high-quality snacks aids in blood sugar stabilization. Keeping a stock of these supplies easily accessible also guarantees that athletes can recover swiftly. Insufficient post-workout nutrition can lead to complications on subsequent training days. In addition, athletes should be cognizant of timing and portion sizes regarding their recovery intake. Utilizing new recovery strategies tailored to meet their specific needs can improve an athlete’s overall performance. When hypoglycemia is appropriately managed through consistent practices, athletes will notice enhancements in energy and performance. This level of attention to diet and recovery shifts the focus from merely completing workouts to optimizing training efficiencies. Continuous evaluation of training routines, nutritional practices, and post-training habits will foster a safer training experience for athletes.
The Importance of Awareness and Support
Understanding the importance of awareness and support structures cannot be overstated. Developing a robust support network that involves coaches, trainers, and medical staff is vital for athletes at any level. This team approach helps create an environment where athletes feel comfortable discussing their needs and concerns. Regular meetings, check-ins, and updates on health status empower the athlete and reinforce personal responsibility over their nutrition and energy management. Moreover, creating a culture that emphasizes education about hypoglycemia fosters resilience. It helps normalize discussions about challenges athletes might face. Prevention and management won’t only enhance performance but safeguard the athlete’s health in the long run. Emphasizing mental sharpness is equally significant; clarity when diagnosing symptoms plays vital roles. Stress management practices that include mindfulness can assist athletes in maintaining focus and calmness during critical moments. All of these elements together facilitate an environment conducive to optimal training outcomes. The collective understanding of hypoglycemia will further aid in promoting healthier habits. Athletes become empowered with knowledge regarding their physiology, focusing on preparedness for training and competition.
The collaboration between nutritionists, coaches, and the athletes is critical for developing personalized strategies that can combat hypoglycemia effectively. Regular assessments help in tracking progress, adapting to changing needs, and refining training methods. It supports the creation of flexible training schedules that accommodate nutrition and recovery. The goal is to do more than prevent hypoglycemia; it’s about fostering complete physical and mental wellness. The more informed athletes are about their body’s responses, the better they can mitigate risks associated with low blood sugar levels. Properly managing hypoglycemia leads not only to improved performance but also to a safer and healthier athletic experience. Encouragement from support networks can motivate athletes to stick to their dietary goals. In high-intensity sports, the edge often lies in small details, and understanding how to manage fatigue can significantly affect outcomes. Comprehensive strategies that create a holistic approach to athletic health can lead to long-lasting impacts on performance. The commitment of athletes to their health should promote their overall athletic journey, making them diligent advocates for their wellbeing.