Understanding the Cardiovascular Benefits of Speed Training
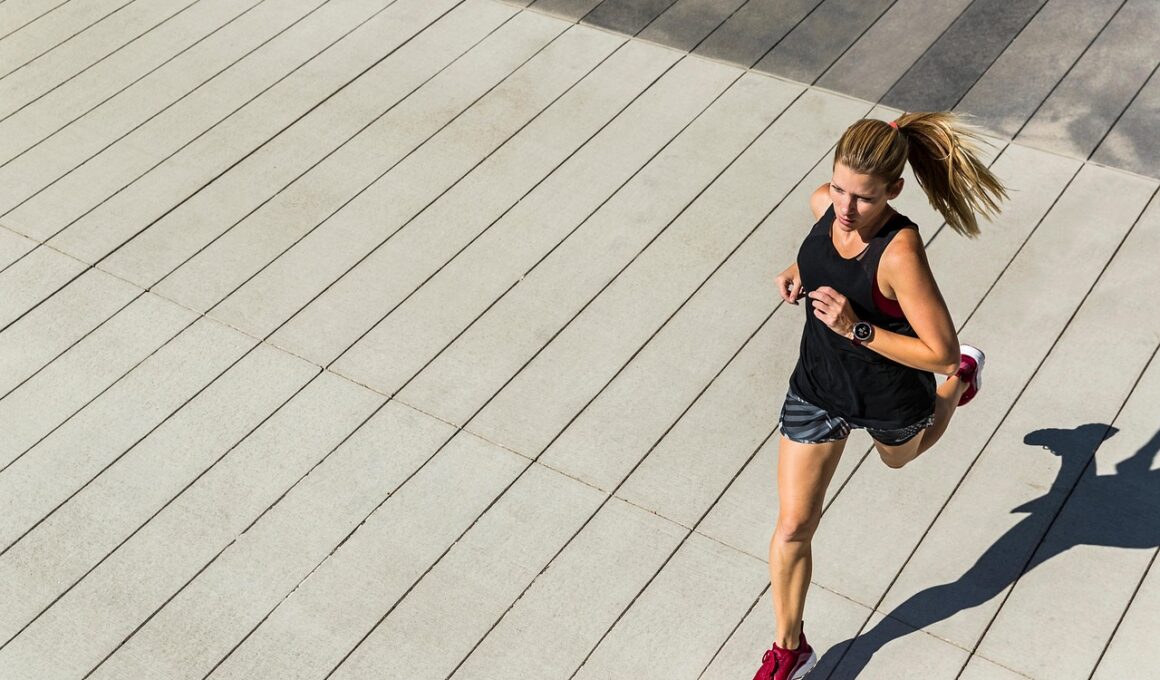
Speed training is a specialized form of exercise emphasizing quick, explosive movements that significantly contribute to enhancing one’s cardiovascular health. When engaging in speed training, the heart and lungs work in unison to deliver oxygenated blood to the muscles, which is crucial for maintaining peak performance. Speed training not only improves cardiovascular function but also increases overall endurance, allowing individuals to perform daily activities with ease. This type of training leads to efficient heart pumping, enhancing stroke volume, which is the amount of blood the heart ejects per beat. Improved stroke volume and heart efficiency help lower the resting heart rate, indicating a stronger cardiovascular system. Additionally, high-intensity speed workouts can yield an impressive caloric burn, facilitating weight management or loss. Incorporating speed training into routine exercise regimens can help prevent various cardiovascular diseases by improving blood circulation and reducing arterial stiffness. The combined physiological effects of speed training on the body create a robust heart, capable of sustaining intense physical activity over extended periods. Hence, understanding the cardiovascular benefits of speed training offers insight into its significance within athletic performance and general physical health.
The Impact on VO2 Max Levels
One of the most significant benefits of speed training is its positive impact on VO2 max levels. VO2 max represents the maximum amount of oxygen utilized during intense exercise and is a crucial indicator of cardiovascular fitness. Enhanced VO2 max can improve endurance, allowing athletes to perform better in competitive settings. Speed training, particularly when combined with interval training, poses challenges that stimulate the body to adapt, increasing aerobic capacity sustainably. This process enhances the cardiovascular system’s efficiency, allowing individuals to transport oxygen more effectively to their muscles. Furthermore, regular speed sessions lead to adaptations at the cellular level, where the body becomes proficient in utilizing oxygen for energy production during strenuous activities. These adaptations are essential for all athletes, regardless of their sport, as better oxygen uptake translates into improved performance and stamina. Additionally, higher VO2 max levels are associated with a lower risk of chronic diseases and cardiovascular issues, reinforcing the necessity of speed training as part of a comprehensive fitness program. Therefore, focusing on improving VO2 max through speed training is essential for enhancing overall physical performance.
Speed training is not solely about the mechanics of running faster or performing better. It profoundly influences heart health by reducing the risk of heart disease, a leading cause of mortality worldwide. Engaging in speed workouts increases heart rate variability, a marker of cardiovascular health. Greater variability is associated with reduced stress levels and improved autonomic nervous system balance. Speed training, especially high-intensity interval training (HIIT), stimulates significant adaptations in the cardiovascular system, leading to improved heart function and increased blood flow throughout the body. Enhanced blood circulation delivers nutrients and oxygen more effectively, facilitating recovery and reducing fatigue. Furthermore, speed training encourages the development of new blood vessels, known as angiogenesis, which enhances the body’s ability to supply oxygen to the muscles. This process is beneficial not just for athletes but for anyone looking to improve their physical health. Additionally, the positive psychological effects of speed training can lead to greater cardiovascular health through increased motivation to stay active. This holistic approach to training underscores the interconnection between physical activity and heart health, making speed training a foundational element of a comprehensive fitness regimen.
The cardiovascular benefits of speed training extend to improved cholesterol and blood sugar levels, contributing significantly to overall heart health. Regular speed training sessions can help raise high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, known as the “good” cholesterol, which aids in preventing atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular issues. Simultaneously, speed training can lower low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, or “bad” cholesterol, reducing the risk for heart diseases. This dual action results in a healthier lipid profile and promotes greater arterial flexibility. Additionally, speed training impacts blood sugar regulation, an essential aspect for individuals with or at risk for type 2 diabetes. Engaging in speed workouts promotes better insulin sensitivity, allowing for more efficient glucose uptake by the cells. This adaptation helps maintain stable blood sugar levels, which is crucial for overall energy management. Combined with a healthy diet, speed training can significantly reduce the risk of metabolic syndrome, characterized by conditions that increase heart disease risk. Therefore, incorporating speed training into one’s fitness routine can serve as a proactive measure for improving heart health and metabolic function.
Enhancing Recovery and Rehabilitation
Another notable benefit of speed training is its role in enhancing recovery and rehabilitation processes within a fitness or athletic context. Regularly incorporating speed training can improve overall muscle recovery, limiting the impact of strenuous workouts on the body. Engaging in speed sessions stimulates blood flow to the muscles, which aids in removing metabolic waste products that accumulate during exercise. Increased oxygen and nutrient delivery accelerate the muscle repair process, ultimately leading to faster recovery times. This is particularly advantageous for athletes prone to injuries, as a significant focus on speed and agility can strengthen muscles and connective tissues, improving resilience against injuries. Furthermore, the controlled nature of speed workouts encourages sustained focus on proper form and technique. This focus can lead to fewer injuries and better long-term performance. For those recovering from injury, speed training can be adapted to accommodate various reconditioning stages, promoting gradual strength development. Thus, speed training serves not only as a tool for enhancing athletic performance but also as a crucial component in rehabilitation programs, catering to individuals returning to physical activity.
Beyond the immediate physiological adaptations that speed training offers, there are heightened mental benefits that contribute significantly to cardiovascular health. Engaging in high-intensity speed workouts can foster psychological resilience, reducing stress and promoting mental clarity. The adrenaline rush during speed training promotes a feeling of euphoria, often referred to as the “runner’s high,” which can elevate mood levels. The mental discipline cultivated through speed training can translate into improved focus and concentration in daily life. Running and sprinting challenges both the body and mind, encouraging participants to push through mental barriers and discomfort. This mental toughness can lead to greater self-efficacy, boosting confidence in various life areas. Furthermore, engaging in a speed training regimen allows individuals to set and achieve personal goals, further enhancing their mental fortitude. This combination of physical exertion and psychological resilience not only improves heart health but also contributes to overall psychological well-being. For many, speed training serves as a valuable outlet for releasing tension and managing stress, emphasizing the profound connection between physical fitness and mental health.
In conclusion, the cardiovascular benefits of speed training are multifaceted and play a vital role in promoting overall health and fitness. From enhancing VO2 max levels to improving cholesterol profiles, speed training contributes significantly to heart health. Moreover, its ability to reduce stress, promote mental resilience, and facilitate recovery makes it an essential component of any fitness program. By integrating speed and agility training into workout routines, individuals can experience enhanced endurance, reduced injury risk, and improved psychological well-being. These benefits reinforce the importance of speed training for athletes and casual fitness enthusiasts alike. As the understanding of its cardiovascular advantages continues to grow, more individuals should consider incorporating speed training into their daily routines. Individuals can foster not only physical improvements but also significant mental health benefits through such efforts. The holistic approach that speed training provides ensures that both body and mind are nurtured, contributing to a balanced and healthier lifestyle. Therefore, understanding and embracing the cardiovascular benefits of speed training can help everyone lead more active and fulfilling lives.