First Aid for Blunt Force Trauma and Associated Bleeding in Sports
In sports, blunt force trauma can lead to significant bleeding and injuries requiring prompt first aid. Athletes can suffer from various types of wounds, ranging from minor cuts to serious lacerations. Recognizing the different types of bleeding is essential for effective treatment. The primary types are arterial, venous, and capillary bleeding, each with distinct characteristics. Arterial bleeding typically involves bright red blood that spurts with each heartbeat. This type denotes a more serious risk and needs immediate attention to prevent severe blood loss. Venous bleeding, on the other hand, usually involves darker blood and flows steadily from a wound, while capillary bleeding is often slow and oozes from surface wounds. Understanding these types enhances the chances of effective intervention during emergencies. Athletes and coaches should be well-informed on how to address injuries calmly and efficiently. Implementing comprehensive first aid training within sports teams can provide a structured response plan. Being aware of the right techniques for bleeding control and wound care is vital for athlete safety. Always have adequate first aid kits available during sports events to tackle injuries quickly and effectively.
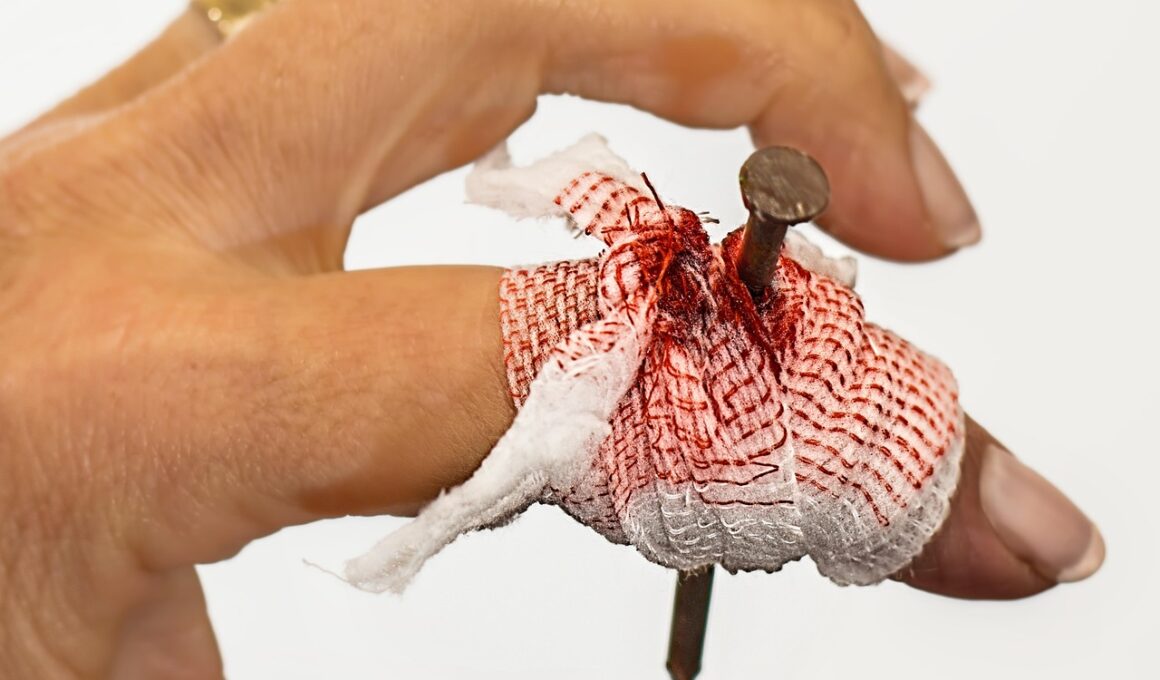
When managing bleeding from blunt force trauma, the first step involves assessing the situation for safety. Ensure that the area is safe for both the injured athlete and responders. Begin by gently applying pressure to the wound using a clean cloth or sterile gauze. This direct pressure helps to control bleeding effectively. If the blood soaks through the cloth, it’s crucial to add more layers without removing the initial dressing. Doing so maintains pressure on the wound site and enhances blood clotting. It’s essential to keep the injured area elevated if possible, as this can reduce blood flow and minimize further bleeding. If bleeding does not stop after several minutes of applying pressure, seeking further medical assistance is critical. Documenting all facts regarding the injury when medical personnel arrives is beneficial for accurate treatment. Athletes should not resume play until they receive a medical evaluation, as further injury could exacerbate their condition. Furthermore, understanding how to recognize shock is also essential as it can occur following severe blood loss. Monitor for symptoms like pale skin, rapid pulse, and faintness, which indicate the need for immediate medical care.
Types of Wound Care
In the treatment of wounds resulting from blunt force trauma, understanding the right approach to care is vital. Initial cleaning of the wound should be done using clean water to remove debris. If the wound is more than a minor scrape, professional medical intervention is advisable. Proper sanitation is crucial to prevent infections, which can complicate recovery. After cleaning, it’s important to cover the wound with appropriate dressings. Adhesive bandages work well for minor cuts, while larger wounds may require gauze along with medical tape. Regularly changing dressings and monitoring for signs of infection, such as redness or discharge, enhances healing. If a wound appears more serious, stitches or staples may be necessary, and this requires a healthcare professional’s assistance. Athletes should educate themselves about keeping their own wounds clean and observing recovery signs diligently. Stitches and proper wound care prevent excessive scarring and enable quicker return to sports. Follow-ups with medical professionals ensure that no complications arise during the healing process, allowing athletes to return safely to their sports.
Recognizing infection signs is important for proper wound healing management. Key indicators of infection include increased redness around the wound, swelling, and warmth. Purulent discharge may also be present if infection has set in. Athletes should be proactive in observing any changes in their wounds. Frequently questioning the appearance and smell of the wound helps in identifying potential issues early on. If an athlete suspects an infection, contacting a medical professional should be the immediate next step. The risk of infections is higher in wounds that are not properly cleaned or dressed. Athletes involved in contact sports are particularly at risk due to the increased chance of dirt and bacteria entering their wounds. In addition to visible signs, efficiency in communication with medical support is crucial to avoid deterioration. Ignoring subtle signs can lead to more complex health issues later. Prompt treatment can make the difference for recovery times and ensure athletes return to their sports in peak condition. Fostering a positive culture around injury reporting is essential to protect athletes’ well-being while they compete.
Preventative Measures
In addition to immediate wound care, taking preventive measures can significantly minimize injury risks in sports. Coaches and athletes should prioritize protective gear that absorbs impacts and enhances safety during play. Proper fitting helmets, shin guards, and pads can help reduce the likelihood of blunt force injuries. Athletes need to be educated on the importance of warm-up routines, which enhance muscle flexibility and strength, thus preventing injuries. Additionally, maintaining proper hydration and nutrition bolsters overall body function, making athletes less susceptible to injury. Players must also be aware of their limitations and avoid pushing beyond their capabilities during practices or games. Clear instruction regarding safety protocols and first aid training can provide effective responses to injuries when they occur. Regular checks on equipment for wear and tear ensure robustness during sports. Finally, instituting emergency action plans within teams allows prompt responses when injuries arise. Training athletes on how to assist their peers during emergencies fosters a supportive team environment. The focus should always be on long-term health and well-being, ensuring athletes remain active for longer periods within their sports.
Understanding the emotional impact of blunt force trauma is equally important as managing physical injuries. Athletes may experience fear, anxiety, or uncertainty regarding returning to play after being injured. Emotional first aid can be just as necessary as physical care. Coaches, teammates, and trainers should be empathetic and provide support during recovery. Encouraging open communication about feelings, fears, and expectations assists athletes in navigating their recovery process more comfortably. Motivational support can foster resilience, enabling quicker mental recovery and facilitating a return to sports. Techniques such as visualization and mindfulness can help athletes cope with stress and rebuild confidence. Engaging with sports psychologists or counselors can provide skills necessary to manage psychological aspects effectively. Informing the athlete about recovery steps and ensuring they have a clear plan decreases anxiety surrounding injuries. Implementing team discussions can create a supportive environment, lessening the stigma around discussing mental health. Overall, addressing both emotional and physical recovery creates a balanced approach to athlete care, focusing on holistic well-being during competition and beyond.
Conclusion
In summary, first aid for blunt force trauma and associated bleeding in sports involves a mixture of immediate care, ongoing management, and preventative measures. Recognizing the various types of bleeding and effectively applying pressure can save lives during acute situations. Following this initial response, ensuring proper wound care is necessary for recovery. Being vigilant about infection signs is essential, as untreated injuries can become complex health issues. Athletes should also understand the emotional aspects related to injuries and work towards building resilience through supportive structures. Preventative measures are equally important to minimize the risk of blunt force trauma during training and competitions. By prioritizing both physical health and psychological well-being, athletes can ensure a robust return to their sporting activities. Continuous education on injury management, first aid training, and teamwork creates a culture of safety. Coaches and athletes alike should commit to ongoing improvement in these areas, as athlete safety is paramount. With effective first aid practices and an emphasis on mental support, athletes can thrive, ensuring both performance and health in their sports engagements.