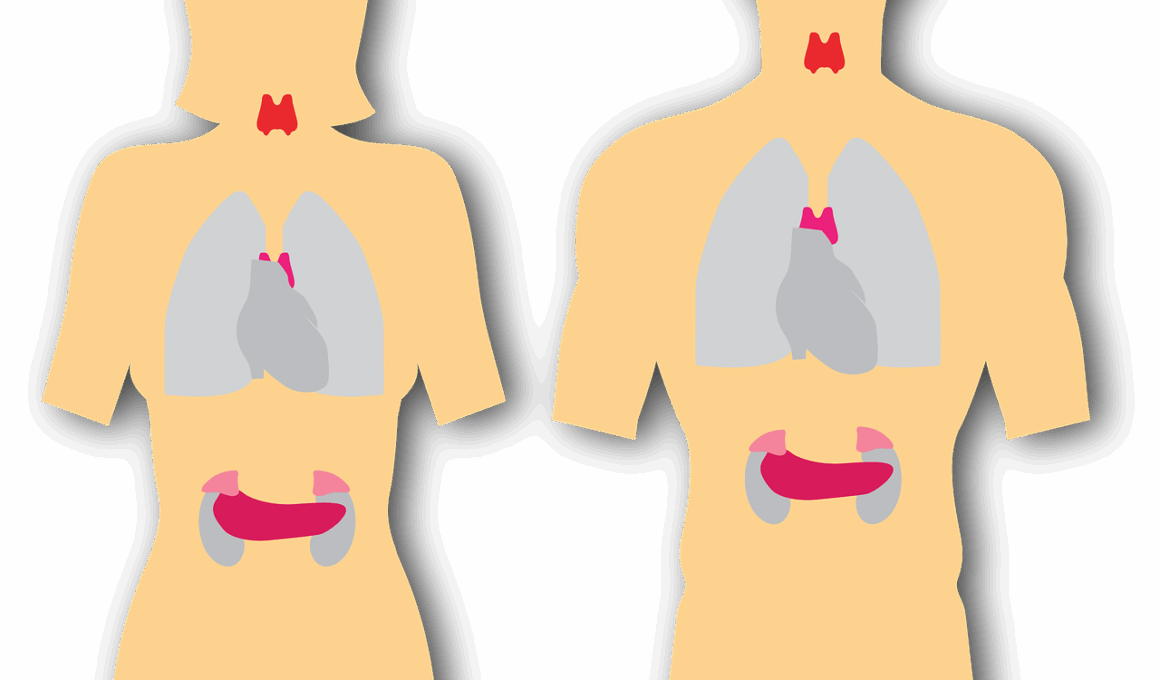Endocrine Disruptors and Their Effects on Body Composition
The human body relies on hormones to regulate various systems, influencing metabolism, growth, and overall health. Endocrine disruptors are chemicals that can interfere with hormone functions, leading to negative effects on body composition. These substances are found in everyday products, such as plastics, pesticides, and personal care items. Research has shown that exposure to these disruptors can lead to weight gain, altered metabolism, and changes in fat distribution. Some of these chemicals mimic natural hormones, causing the body to respond incorrectly. For instance, they can lead to an increase in fat tissues or result in hormonal imbalances, particularly affecting insulin and cortisol levels. Lower levels of testosterone in men and higher levels of estrogen in women can exacerbate body composition issues. Thus, understanding the impact of endocrine disruptors is crucial for maintaining a healthy body weight and composition. By reducing the exposure to these harmful substances, individuals may improve their hormonal balance and overall physical health. Therefore, awareness and lifestyle changes are necessary for combating the impact of these harmful chemicals.
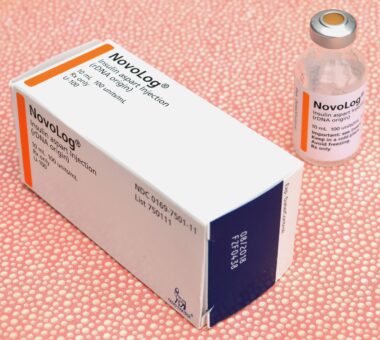
Hormones play a vital role in the regulation of body fat and lean body mass, influencing various processes such as appetite, energy expenditure, and fat storage. Key hormones involved include insulin, leptin, and ghrelin. Insulin, secreted by the pancreas, regulates glucose levels in the blood and promotes fat storage. Leptin, produced by fat cells, signals the brain when to stop eating, while ghrelin stimulates appetite. Disruption of these hormones can lead to overeating and weight gain. For example, increased exposure to endocrine disruptors can cause changes in leptin levels, resulting in impaired satiety signals. Furthermore, ghrelin levels can be affected by stress and environmental toxins, prompting increased hunger and potential weight gain. The complex interplay among these hormones highlights the intricate balance required for healthy body composition. When this balance is disrupted, individuals may experience difficulties in managing weight and maintaining a healthy body fat percentage. Consequently, addressing the influence of endocrine disruptors on these hormones is essential for improving body composition and overall health.
The Impact of Endocrine Disruptors
Numerous studies have indicated that exposure to certain endocrine disruptors can negatively affect body composition, primarily through obesity and metabolic syndrome. These conditions involve an increase in fat mass and alterations in fat distribution. For instance, bisphenol A (BPA), commonly found in plastic containers, mimics estrogen, leading to increased fat absorption and storage. In addition, phthalates, used in various consumer products, can disrupt testosterone production in men, further contributing to obesity. Research has shown that populations exposed to high levels of these chemicals often present with increased body fat, especially visceral fat. This type of fat surrounds vital organs and is associated with various health risks. Reducing exposure to these substances can lead to improvements in metabolic health and body composition. Public awareness of the effects of endocrine disruptors has spurred some changes in regulations, encouraging manufacturers to consider safer alternatives. Individual choices, such as consuming organic foods and removing plastic storage containers, can also help minimize exposure, thus supporting a healthier hormonal environment for maintaining optimal body composition.
Endocrine disruptors are not only affecting adults, but they also have significant implications for children and adolescents. These age groups are in critical stages of development, making them more susceptible to the effects of hormonal interference. Early exposure to chemicals like bisphenol A (BPA) or organophosphate pesticides can have lasting impacts on metabolism, growth rates, and body composition. Research shows a correlation between such exposures and increased instances of obesity in children. Disrupted hormone levels can result in early onset of puberty, which also influences body composition changes. Furthermore, nutritional habits established during childhood can lead to long-term health outcomes, affecting adult body composition. Awareness among parents regarding these substances is vital for protecting the next generation from unintended health consequences. By choosing safer products and educating children on the importance of nutrition and physical activity, we can mitigate the effects of endocrine disruption. Thus, proactive measures are needed to ensure healthy growth and development during these formative years, emphasizing the critical connection between environmental exposures and long-term health.
Strategies for Minimizing Exposure
To combat the negative effects of endocrine disruptors on body composition, individuals can adopt strategies to minimize exposure. Firstly, becoming knowledgeable about potential sources of these chemicals is crucial. One effective approach is to reduce the use of plastic products or opt for BPA-free alternatives. This includes using glass or stainless steel containers for food storage and avoiding canned foods lined with plastic. Additionally, consumers can improve their diets by choosing organic foods, which are less likely to contain pesticide residues that disrupt hormonal balance. Furthermore, increasing the intake of fruits and vegetables can enhance detoxification, promoting the elimination of harmful substances from the body. Regular physical activity also plays a significant role in maintaining hormonal balance and counteracting weight gain. Engaging in exercise can support metabolic health and help mitigate the effects of endocrine disruptors. Ultimately, creating a safer living environment is a collective effort that not only benefits individual health but also contributes to broader public health outcomes.
Research into the effects of endocrine disruptors is ongoing, with scientists continually investigating their mechanisms and long-term impacts on health. Understanding how these chemicals interact with hormonal systems can lead to better prevention strategies for adverse health effects, such as unwanted body composition changes. Studies have focused on different populations, analyzing data to identify correlations between exposure levels and prevalent health conditions. Further research is needed to establish definitive links between specific endocrine disruptors and their effects on body composition. In addition, evaluating potential synergistic effects of multiple exposures is essential. As findings emerge, guidelines and recommendations may evolve to protect individuals, particularly vulnerable populations like pregnant women and children, from harmful exposures. Increased funding for studies focused on endocrine disruption can also aid in raising awareness and shaping public policy. Ultimately, continued exploration will enhance understanding and pave the way for better health outcomes, promoting overall well-being in society.
Conclusion
The role of hormones in body composition highlights the significance of reducing exposure to endocrine disruptors. These harmful chemicals can interfere with hormonal balance, potentially resulting in weight gain, hormonal imbalances, and adverse metabolic effects. By acknowledging the sources of these disruptors and taking necessary actions to minimize exposure, individuals can promote better body composition and overall health. Solutions lie in making informed choices about daily products, foods consumed, and lifestyle practices. Awareness among consumers about the implications of these disruptors is crucial for creating healthier environments for themselves and future generations. Advocacy for stricter regulations regarding the use of harmful substances is also essential. As our understanding of the relationship between endocrine disruptors and body composition evolves, individual and collective efforts can lead to a healthier, balanced life. Education, preventive measures, and community engagement will play vital roles in addressing this public health challenge. Together, we can pave the way toward improved health and well-being by fighting against the detrimental effects of endocrine disruptors.
Hormones play a vital role in the regulation of body fat and lean body mass, influencing various processes such as appetite, energy expenditure, and fat storage. Key hormones involved include insulin, leptin, and ghrelin. Insulin, secreted by the pancreas, regulates glucose levels in the blood and promotes fat storage. Leptin, produced by fat cells, signals the brain when to stop eating, while ghrelin stimulates appetite. Disruption of these hormones can lead to overeating and weight gain. For example, increased exposure to endocrine disruptors can cause changes in leptin levels, resulting in impaired satiety signals. Furthermore, ghrelin levels can be affected by stress and environmental toxins, prompting increased hunger and potential weight gain. The complex interplay among these hormones highlights the intricate balance required for healthy body composition. When this balance is disrupted, individuals may experience difficulties in managing weight and maintaining a healthy body fat percentage. Consequently, addressing the influence of endocrine disruptors on these hormones is essential for improving body composition and overall health.