Recognizing Hypoglycemia in Youth Athletes
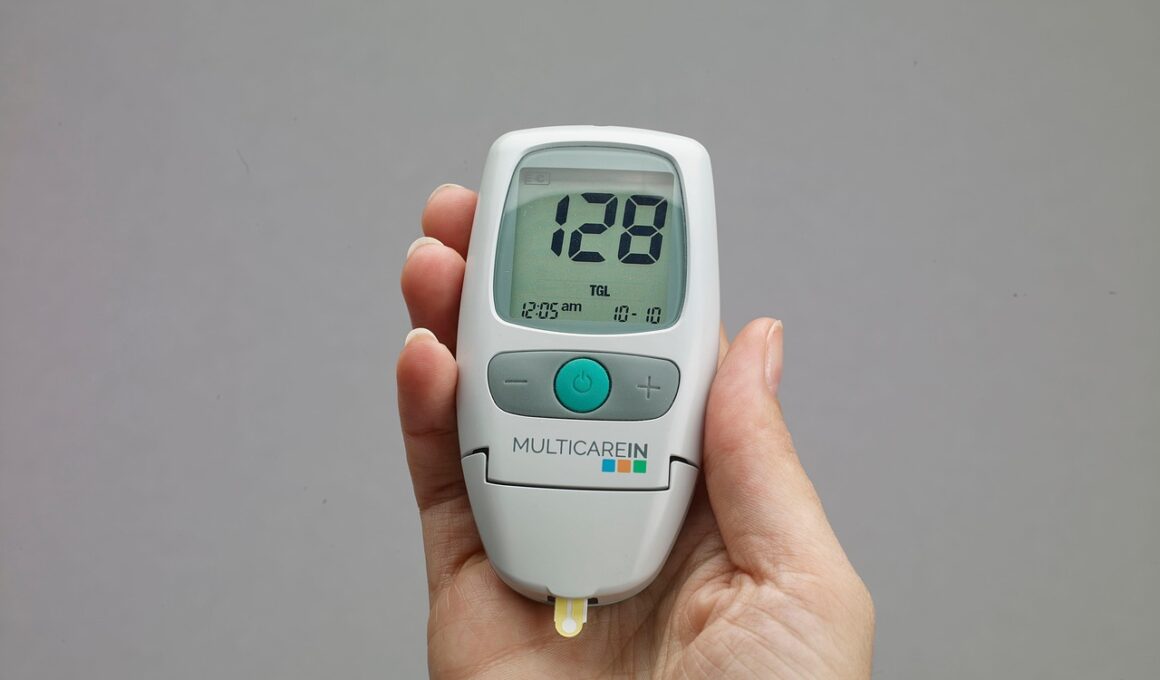
Hypoglycemia in athletes, particularly youth athletes, can be a serious concern during activities that require considerable energy expenditure. It occurs when blood glucose levels drop significantly, causing adverse symptoms that can affect performance and safety. Recognizing early signs is crucial for timely intervention. Symptoms may include shaking, sweating, confusion, irritability, and intense hunger. Athletes might also experience dizziness and fatigue, which could ultimately impair their performance. Coaches and parents need to be alert for these signs during practice and competition. Education on this condition is vital to ensure that athletes can effectively communicate their symptoms to coaches or medical staff. Prompt management is necessary to prevent severe outcomes, including loss of consciousness. It may be beneficial to create a protocol for quick intervention involving glucose supplements or snacks high in carbohydrates. Ensuring that hydration levels are adequate is equally important. Sports drinks designed for rehydration can also support glucose levels, providing a dual benefit. Parents of young athletes should work closely with healthcare providers to develop a strategy suited to their child’s specific needs while participating in sports activities, especially those known to be rigorous and demanding.
Understanding the Causes of Hypoglycemia
Several factors contribute to hypoglycemia in youth athletes, including inconsistent eating habits, excessive physical activity without adequate energy intake, and underlying health conditions. Youth may sometimes skip meals or snacks, assuming they can compensate through their activity levels. Inadequate carbohydrate consumption before and during participation in sports can profoundly impact energy levels, leading to severe drops in blood sugar. Further, intense training sessions often increase the body’s demand for glucose, leaving younger athletes vulnerable to hypoglycemia when they do not replenish their stores. Additionally, some may be predisposed to hypoglycemic episodes due to medical conditions, such as diabetes. Parents and coaches should consider maintaining a consistent and balanced pre-activity meal schedule that includes complex carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats. Furthermore, a diet rich in these nutrients can support sustained energy levels throughout training or competition. Recognizing the interplay between nutrition and exercise is critical to preventing hypoglycemia. Involving a nutritionist to support dietary planning for young athletes can ensure they meet their energy and performance requirements on training and competition days, ultimately enhancing their overall athletic performance.
Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
The signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia in youth athletes vary from mild to severe and can progress quickly if unaddressed. Coaches must familiarize themselves with these symptoms to ensure prompt action. Mild symptoms include sweating, trembling, and feelings of extreme hunger. As athletes experience a further decline in blood glucose, they may exhibit confusion or mood changes, becoming irritable. Physical symptoms can include weakness, severe exhaustion, headaches, and rapid heartbeat. Coaches and parents should educate young athletes about these signs, encouraging them to be aware of their bodies and communicate effectively. Monitoring performance is essential, as unexplained decreases in performance may indicate a drop in blood sugar levels. Conducting regular check-ins during long practice sessions or games can be advantageous. If hypoglycemia is suspected, an immediate carbohydrate source, such as glucose tablets or a sugary snack, should be provided if the athlete is conscious and able to swallow. In cases of severe hypoglycemia leading to unconsciousness or seizures, emergency medical assistance must be sought without delay. Awareness and education play critical roles in ensuring safety among youth athletes, making early recognition an indispensable skill for those involved.
Immediate Management Strategies
Quick intervention is necessary to manage hypoglycemia effectively. If young athletes experience the symptoms previously identified, immediate access to a fast-acting carbohydrate source is essential. Simple sugars such as candy, fruit juice, or glucose tablets can quickly elevate blood sugar levels. It is critical to monitor the athlete closely after administering carbohydrates to see if symptoms improve. Typically, improvement is expected within fifteen to twenty minutes. If symptoms persist or worsen, further evaluation by a healthcare provider may be required. It may also be helpful for coaches and parents to develop an action plan for hypoglycemia management, which outlines steps to follow when students exhibit symptoms before, during, or after intense exercise. This plan can include graphing blood glucose levels and regularly scheduled check-ins during training sessions or games. Equipped with knowledge and strategies, coaches will feel more competent in handling these situations effectively, helping young athletes grow with confidence in their abilities. By providing structured guidance, coaches prevent serious complications and ensure that each child has the support they need during their physical activities, leading to better overall performance.
Long-term Considerations for Energy Balance
Maintaining an optimal energy balance is vital for youth athletes to minimize the risk of hypoglycemia. Energy balance refers to the equilibrium between food intake and energy expenditure during physical activity. Adopting healthy eating habits is crucial in achieving this balance. Structured meals and healthy snacks before and after training sessions or events can significantly impact energy levels and overall performance. Athletes should be encouraged to develop a meal plan that accounts for their training schedule, ensuring sufficient fuel before exertion. Meals high in complex carbohydrates contribute to sustained energy release while proteins facilitate recovery afterwards. Meeting hydration needs is equally essential in maintaining energy balance. Proper hydration supports all physiological functions, including metabolism and energy availability. Parents may find it helpful to engage with a sports nutritionist to devise a tailored meal plan addressing their young athlete’s activity levels and personal preferences. This strategy helps ensure all nutritional needs are met to promote optimal performance while minimizing the risk of hypoglycemia. By encouraging a lifestyle that considers nutrition and activity, youth athletes will learn to prioritize their health, ultimately enhancing their overall athletic experiences.
The Role of Coaches and Educators
Coaches and educators play a pivotal role in monitoring young athletes and providing necessary support regarding health management practices. Establishing open communication lines between athletes, coaches, and parents helps foster a supportive environment where everyone can share insights about nutrition and hydration. Coaches should prioritize education about the causes, signs, and management of hypoglycemia within their teams. Regular workshops or informational sessions can help demystify this condition, aiding in the empowerment of young athletes and their families. Incorporating preventive strategies into training regimens can further reinforce the importance of nutrition and self-monitoring. Establishing team norms around hydration and nutrition encourages all athletes to adhere to safe practices and recognize hypoglycemia’s implications. By advocating for a holistic approach to athlete health, including educational initiatives, coaches can empower young athletes to take charge of their health and performance. Everyone involved in children’s sports should work together to create a comprehensive support network. This collaboration enhances awareness surrounding hypoglycemia and ultimately leads to healthier, better-performing young athletes who enjoy participating in their chosen sports.
Conclusion: Prioritizing Athlete Health
Understanding and managing hypoglycemia among youth athletes is essential for ensuring their safety and success in sports. Through education, awareness, and proactive measures, athletes can significantly reduce the risk of experiencing hypoglycemic episodes. It is vital to emphasize that regular, nutrient-dense meals and healthy snack practices must be upheld. Promoting an environment where young athletes feel comfortable discussing their health and performance concerns is crucial. This approach not only enhances athlete performance but also fosters a lasting appreciation for healthy habits throughout life. Coaches, parents, and educators must collaborate to craft effective strategies that prioritize athlete well-being, including nutrition education, hydration awareness, and tailored fitness programs. By approaching hypoglycemia with a comprehensive understanding and commitment to athlete health, we nurture the growth of capable, knowledgeable, and resilient young athletes. In conclusion, investing in their health today leads to improved athletic performance and a lifetime of positive habits beyond their years in competitive sports.
Further Reading and Resources
For those interested in further exploring the complexities of hypoglycemia in youth athletes, many resources are available. Books and articles on sports nutrition can expand understanding of appropriate meal planning strategies specific to active individuals. The American Academy of Pediatrics provides guidelines on healthy eating habits for athletes and offers a plethora of useful information. Consulting with a registered dietitian specializing in sports nutrition can provide individualized guidance for young athletes. Furthermore, workshops and seminars aimed at athletes, coaches, and parents can promote awareness and best practices for managing hypoglycemia. Seeking support from local sports organizations or health-focused nonprofits can connect families with additional resources dedicated to athlete health. Overall, empowering youth athletes through education is key to preventing and managing hypoglycemia effectively. By engaging with various resources, stakeholders can equip themselves and their athletes with the tools necessary for a successful sports journey, ensuring optimal health and performance in athletic experiences.