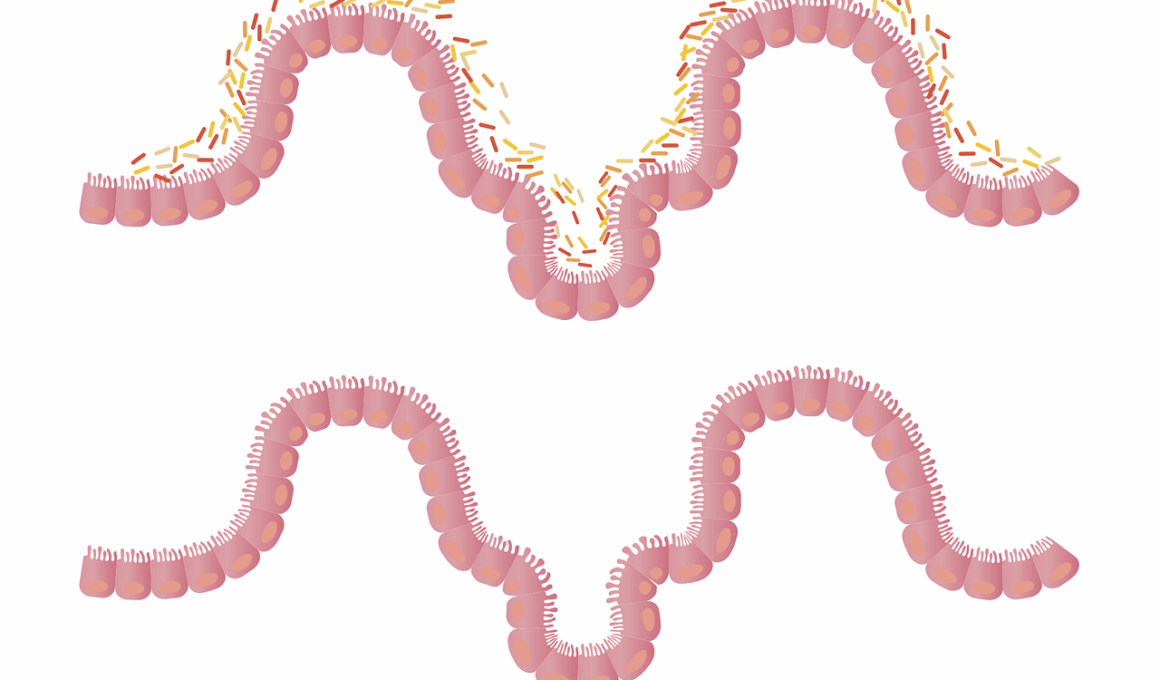
The Influence of Gut Health on Supplement Safety Profiles
In recent years, research has significantly highlighted the relationship between gut health and the safety profiles of dietary supplements. The gut microbiome plays a pivotal role in how our body absorbs nutrients, metabolizes substances, and responds to various supplements. An imbalance in gut bacteria can lead to negative interactions when supplements are ingested. When supplements, containing herbs or vitamins, are introduced into a compromised microbiome, they could lead to adverse effects. Additionally, the composition of one’s gut flora can influence the bioavailability of active ingredients in supplements, making gut health a critical factor for efficacy and safety. The safety profile of supplements could drastically change depending on whether the gut environment is conducive for optimal nutrient processing. Therefore, there is an increasing movement within the scientific community to focus on personalized nutrition approaches that consider individual gut microbiomes. Having a tailored supplement regimen could enhance biochemical outcomes while reducing the risk of adverse health effects. More research is required to fully understand the connection, paving the way for the design of future supplements that align safely with specific gut health parameters.
As research continues to evolve, it has become clearer that supplements are not a “one-size-fits-all” solution. Each individual presents unique gut health profiles that can alter how supplements are metabolized. Personalized supplement formulations reflect a growing trend in addressing individual health issues more precisely, particularly regarding the gut microbiome’s composition. This approach allows for the selection of supplements that work synergistically with one’s natural gut flora, leading to improved absorption and minimized side effects. Moreover, understanding the potential influence of various dietary components on gut health can enhance supplement safety. For example, prebiotics and probiotics are increasingly included in dietary supplements, supporting gut health while also offering additional health benefits. The integration of these elements not only promotes a healthier gut environment but also drastically enhances the body’s response to supplements. Differentiating supplements based on individual microbiome analyses may assist clinicians and consumers alike in making informed decisions. This comprehensive view presents a shift in how supplements are perceived; they should not merely treat deficiencies but also promote overall wellness. A closer look at gut health reveals that it is foundational to enhancing supplement efficacy.
The implications of gut health extend further into the realm of chronic diseases treated with supplements. Individuals suffering from conditions like diabetes, inflammation, or autoimmune disorders may respond differently to supplements based on their gut microbiota. For instance, certain amino acids and omega-3 fatty acids are utilized differently in a healthy microbiome than in one affected by dysbiosis. This leads to significant variations in therapy responses and emphasizes the urgency for more innovative studies directed toward understanding these different interactions. Implementation of microbiome analysis can also inform dosing recommendations, ensuring that patients are not unintentionally underdosing or overdosing. Additionally, many popular dietary supplements are derived from natural sources, which can vary in their chemical composition based on growth circumstances and handling methods. Monitoring for contaminants like heavy metals or unwanted additives in supplements becomes even more critical when personalized supplements come to light. Product safety regulations must adapt to the emerging science so that only the safest, most effective formulations are available. More rigorous approval processes for supplement companies that consider gut health interactions could safeguard consumer health while promoting beneficial products.
Challenges in Supplement Safety Research
Despite advancements, several challenges persist concerning the study of gut health and supplement safety. The complexity of the gut microbiome makes it difficult to establish universal guidelines suitable for all. Individual variations in gut profiles and dietary habits contribute to a convoluted picture, leading to unreliable data and conclusions. Moreover, current safety assessment methods often overlook microbiome factors during evaluations. Many existing supplement safety studies tend to focus almost exclusively on chemistry, ignoring biological responses influenced by gut health. As such, the insights generated might not reflect actual outcomes experienced by everyday users. The necessity of standardized testing frameworks that incorporate gut health metrics is paramount. Additionally, the limitations on human testing can skew data. Ethical considerations frequently prevent larger-scale human trials. This leads to a reliance on animal studies, which may not accurately mimic human responses. Furthermore, lack of funding for gut health-related research is an ongoing obstacle, limiting the depth and breadth of investigations. Addressing these challenges through interdisciplinary collaboration will push forward the frontiers of supplementary safety strategies based on individual microbiome assessments.
Consumer awareness regarding the safety and efficacy profile of supplements largely revolves around health claims. As individuals seek to boost their wellness via nutrition, understanding the connection between gut health and supplements becomes crucial. Many consumers are becoming more proactive in researching products, often gravitating toward those that highlight probiotic and prebiotic content on labels. This heightened awareness is beneficial as understanding the importance of gut health invites a more critical examination of dietary supplements. Consumers who are well-informed about their gut health are more likely to opt for scientifically-backed products. In addition, there is an increasing number of platforms and resources that educate individuals about gut health, allowing them to make informed choices. Consequently, some manufacturers may pivot their marketing strategies, accommodating this demand for gut health-focused supplements. However, the risk remains that misinformation or exaggerated claims may mislead consumers seeking legitimate solutions. An informed consumer base can encourage manufacturers to maintain high safety and quality standards, driving positive product development while prioritizing genuine health benefits. Cultivating a well-informed public will help create a market that celebrates transparency and integrity in supplement safety.
The Future of Supplements in Relation to Gut Health
As our understanding of gut health expands, the future of supplements appears promising yet complex. Ongoing research will likely lead to the development of next-generation supplements specifically designed to align with diverse gut microbiomes. Scientists are exploring ways to incorporate precision medicine practices that will allow for customization based on an individual’s gut flora. Innovations may lead to supplements that synergistically act with gut bacteria, enhancing their efficacy while minimizing risks. Furthermore, the integration of technology, such as smartphone applications to track dietary intake and gut health, may allow consumers to personalize their supplement choices dynamically. These advancements represent a shift towards a preventive health model where supplements serve as preventive measures rather than merely corrective ones. Future formulations may incorporate diversity in ingredients that take into account metabolic pathways influenced by gut health. This personalized supplementation trend can revolutionize not only dietary habits but also overall health maintenance strategies, potentially impacting public health positively. As the pursuit for smarter, safer supplements continues, the interdisciplinary collaboration between dietitians, scientists, and healthcare professionals becomes critical in shaping responsible practices.
In conclusion, the influence of gut health on the safety profiles of supplements is an emerging area of research with transformative potential. Understanding how gut microbiota interacts with various dietary components is essential for ensuring consumers’ health and wellness. This shift towards personalized nutrition, centered around individual gut health, highlights the importance of effective absorption and safety in supplement use. By learning how various products interact with gut health, consumers can make informed decisions, driving improvements in product safety and efficacy. Rising consumer education and awareness around the principles of gut health are pressing manufacturers to elevate their standards, fostering an environment that prioritizes health at every level. The future of dietary supplements must be rooted in precise formulations that consider unique microbiomes, moving beyond broad-spectrum solutions. Building upon these developments will require commitment and innovations across sectors to create the safest and most effective products. As we align supplement development with gut health understanding, we can contribute to better health outcomes for consumers globally. The ongoing research advocates for continued exploration, inviting broader interest in how diet, gut health, and supplements intertwine.
As consumers and researchers alike delve deeper into understanding dietary supplements, they discover more complexities associated with gut health. Choosing supplements that align with individual gut conditions offers new solutions for health challenges. Ensuring supplement safety by recognizing how gut health impacts absorption and efficacy can lead to a significant reduction in adverse effects. Formulation design considering gut interactions may uncover groundbreaking opportunities in health improvement, fundamentally altering supplement consumption approaches. Consequently, this development signifies a broader understanding of nutrition within the realm of holistic health. Emphasizing gut health alongside the safety aspects of supplements advances the narrative around personal wellness. More rigorous scientific criteria for safety validation linked to gut conditions will empower consumers, ensuring they make choices reflecting their unique health profiles. Additionally, public health initiatives could benefit from emphasizing the link between nutrition and gut microbiome stability. Efforts directed at enhancing nutritional literacy surrounding the microbiome offer potential pathways for improving community health standards. This combined approach, emphasizing both safety and gut health, underscores the urgency for regulatory frameworks to adapt promptly to future challenges and innovations in dietary supplements.