Injury Epidemiology in Professional Sports
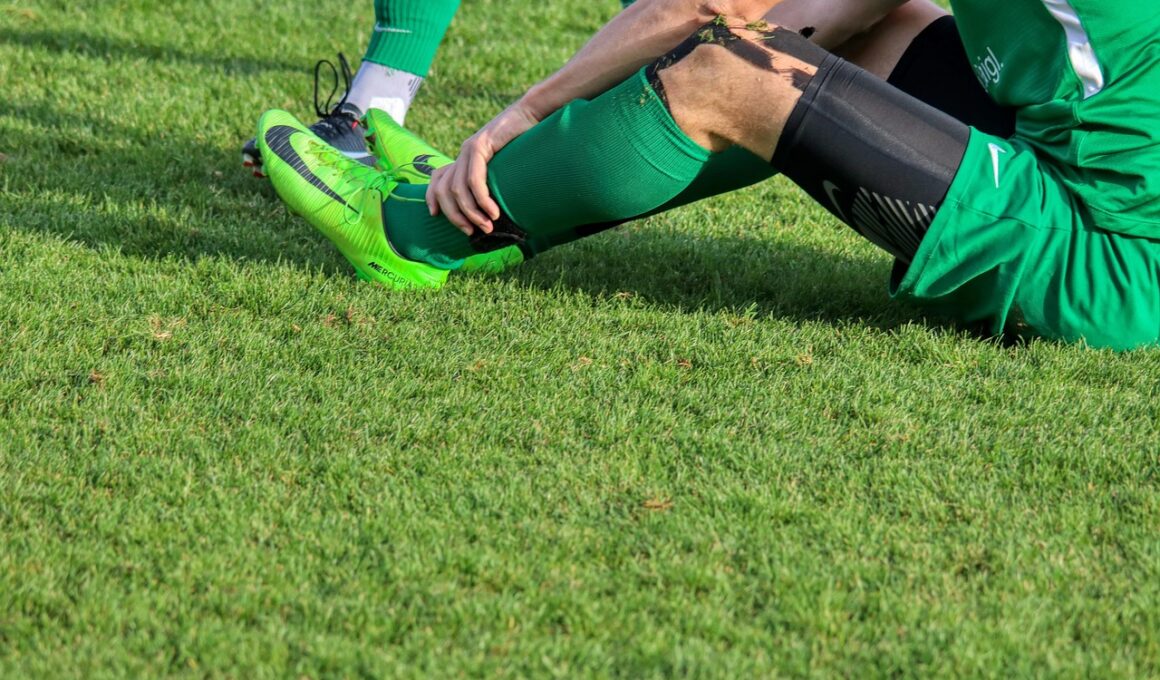
Sports medicine is a vital field focusing on the health, performance, and care of athletes. A significant area of research has emerged around the epidemiology of sports injuries, particularly in professional sports. Such research aims to understand the prevalence, risk factors, and impact of injuries sustained by athletes. Through rigorous data collection and analysis, researchers can track injury patterns, helping to uncover trends across different sports disciplines. The outcome of this research serves multiple purposes, including improving management strategies for injuries and implementing preventive measures. In professional settings, understanding the types of injuries commonly observed enables health professionals to devise tailored interventions. Important factors considered in these studies include athlete demographics, the specific sport played, and the intensity of competition. Each of these elements influences the likelihood of injury occurrence significantly. Furthermore, analyzing injuries allows professionals to address long-term consequences on athletic performance and overall health, emphasizing the need for comprehensive care. Ultimately, the insights gleaned from such epidemiological studies guide policy decisions, enhance coaching methods, and elevate sports safety standards globally, fostering an environment where athletes can perform at their best while minimizing injury risks.
In professional team sports, the occurrence of injuries varies widely among athletes, influenced by sport type, position played, and level of exposure. Research continues to show that contact sports, such as football, rugby, and ice hockey, tend to report higher incidences of injuries compared to non-contact counterparts like swimming or track and field. The nature of contact sports inherently increases risk factors including tackles, collisions, and falls. More specifically, common injuries in such sports can range from concussions to joint injuries, often incurring significant recovery time. Conversely, non-contact sports can still pose injury risks, primarily through repetitive strain or overuse injuries. Athletes must be educated on potential injury risks and the importance of proper training techniques, warm-ups, and cool-downs. Moreover, research on injury prevention strategies has shown that implementing sport-specific training and conditioning can mitigate risk effectively. As teams focus on performance enhancement, integrating strength and conditioning programs specifically designed to address identified vulnerabilities is crucial. By doing so, the likelihood of sustaining injuries decreases significantly, enabling athletes to compete more effectively and safely over extended periods. This proactive approach is essential for enhancing athlete longevity and enjoyment of their respective sports.
Analyzing Injury Data
Numerous data sources are utilized in researching sports injuries, including athlete medical records, injury reports, and retrospective studies. These sources can provide insight not only into injury types but also into the circumstances under which injuries occur. Data collected may include the prevalence of acute versus chronic injuries, tracking through comprehensive cohort studies that monitor athletes over time. Furthermore, sports leagues and organizations implement injury surveillance programs, gathering data systematically across seasons. Such approaches allow for robust statistical analysis, identifying significant patterns and risk factors associated with injuries. Collaboration among various stakeholders, such as team physicians, trainers, and researchers, facilitates a more thorough understanding of injuries. Capturing comprehensive data is paramount for effective injury surveillance, contributing to timely interventions and safety protocols. Research findings can directly influence coaching strategies, training regimens, and safety equipment standards that teams must adhere to. Adaptations based on empirical data can lead to modified rules or gameplay strategies that create safer environments for athletes. Additionally, sharing findings with the wider sports community fosters an atmosphere focused on ongoing improvement in athlete safety measures, ultimately enhancing the quality of professional sports.
One of the primary focuses in sports injury research is the examination of risk factors contributing to injury occurrence. Studies often categorize risk factors as intrinsic or extrinsic, which helps researchers understand underlying conditions or external pressures faced by athletes. Intrinsic factors encompass individual attributes such as age, gender, physical fitness, and previous injury history. In contrast, extrinsic factors may include environmental considerations, equipment quality, and competition level. Understanding these risk factors enables healthcare professionals to develop tailored interventions aimed at injury prevention. Addressing intrinsic factors might involve enhancing athlete fitness through strength training or flexibility exercises, significantly decreasing injury vulnerability. Additionally, utilizing sport-specific training programs allows athletes to adapt to the physical demands of their respective sports. On the other hand, extrinsic factors necessitate a close examination of playing conditions, including weather and field surface quality, which may significantly influence injury risks. Encouraging communication between athletes and coaches also serves as a proactive measure to promote awareness regarding risk factors and training best practices. A multi-faceted approach accounting for both intrinsic and extrinsic risk factors ultimately equips athletes with a better understanding of their unique injury profiles, fostering an environment of safety and care within the sports community.
Preventive Measures
As awareness of sports injuries and their impact grows, preventive measures have gained traction within professional sports. Emphasizing injury prevention aligns with the overarching goal of preserving athlete health and improving performance longevity. Multiple strategies focus on enhancing overall athletic preparedness, reducing injury risk significantly. One effective approach includes educating athletes about proper conditioning techniques and the significance of gradual training progression. Athletes must recognize the importance of warming up and cooling down, optimizing muscle readiness. Moreover, balance and coordination training can enhance an athlete’s proprioception, substantially decreasing the chance of sustaining injuries during performance. Additionally, developing sport-specific drills helps in honing skills relevant to their competitive discipline, yielding better preparedness against injuries. Equipment modifications and advancements also play an essential role in prevention strategies. Ensuring athletes use appropriate safety gear, such as helmets and pads in contact sports, significantly mitigates risk factors. Furthermore, advisors from sports medicine professionals can guide athletes to make informed decisions about their training regimes, nutrition, and recovery protocols. These collaborative efforts foster a protective framework for athletes, allowing them to pursue their sporting career while prioritizing safety and health outcomes.
Understanding the consequences of sports injuries extends beyond immediate physical ramifications, affecting psychological and social aspects of an athlete’s life. Injuries can lead to emotional challenges such as frustration, anxiety, and depression, which can hinder overall well-being. Athletes often face significant psychological stress, especially when they are sidelined from competition due to injury. Research suggests that mental health plays a crucial role in recovery and rehabilitation; thus, comprehensive care must consider both physical and emotional aspects of treatment. Support networks are essential in helping injured athletes cope with setbacks; they may include teammates, coaches, and sports medicine professionals. Encouraging effective communication about emotional struggles fosters an environment where athletes feel secure discussing their experiences. To address psychological issues, sports psychologists may be engaged to provide targeted interventions and coping strategies. Fostering resilience during the recovery phase is critical to minimizing negative impacts on general health. Integrating mental health support into rehabilitation processes allows for a more holistic approach to injury recovery. Ultimately, recognizing the multifaceted consequences of injuries equips professionals to create well-rounded care plans prioritizing the athlete’s overall well-being and future performance potential.
The Future of Research
The landscape of sports medicine research is continuously evolving, particularly within the realm of injury epidemiology. Advancements in technology are driving new methodologies for studying injuries, enabling enhanced data collection and analysis. For instance, wearable technology provides real-time insight into athletes’ biomechanics and workload, allowing nuanced assessments of injury risk. By tracking metrics such as heart rate, movement patterns, and recovery times, researchers can develop predictive models that inform preventive measures. Future studies are likely to focus on the role of genetics in injury susceptibility, examining how individual biological factors influence injury risk. Additionally, interdisciplinary collaboration continues to grow, integrating perspectives from fields such as biomechanics, psychology, and nutrition science to achieve comprehensive insights. Emphasizing the importance of injury prevention in training, new protocols may emerge that dynamically adapt to an athlete’s specific needs. Increased investment in research-focused initiatives by sports organizations can lead to improved funding for injury studies. As more research surfaces, the knowledge gained will not only protect athlete health but also influence regulations and guidelines governing sports globally. Consequently, the commitment to advancing injury epidemiology promises to ensure athletes remain at the forefront of safety and performance excellence.
In conclusion, injury epidemiology is an essential aspect of sports medicine, concentrating on the prevalence, causes, and implications of sports injuries. By delving into the specifics of injury occurrence within professional sports, researchers contribute to a better understanding of how to protect athletes effectively. Integrating data analysis, prevention strategies, and holistic rehabilitation models is essential for fostering an environment where athletes can thrive. Awareness and education surrounding the importance of safe practices, nutrition, and mental health must be emphasized across all levels of sport. Furthermore, by promoting interdisciplinary collaborations, stakeholders can address injury risks comprehensively, ultimately enhancing athlete health outcomes. Ongoing research endeavors must focus on emerging trends, ensuring that preventive measures keep pace with the evolving landscape of professional sports. As innovations in sports medicine continue to surface, the future looks promising for reducing injury occurrences, ensuring athletes are equipped to perform at their best. Ultimately, safeguarding athletes fosters a culture in sports that prioritizes well-being, encouraging participation and excellence. The commitment from every member of the sports community is vital to shaping a healthier, safer future for athletes everywhere, paving the way for ongoing enhancements in sports injury research and care standards.