Functional Training Adaptations for Arthritic Joints
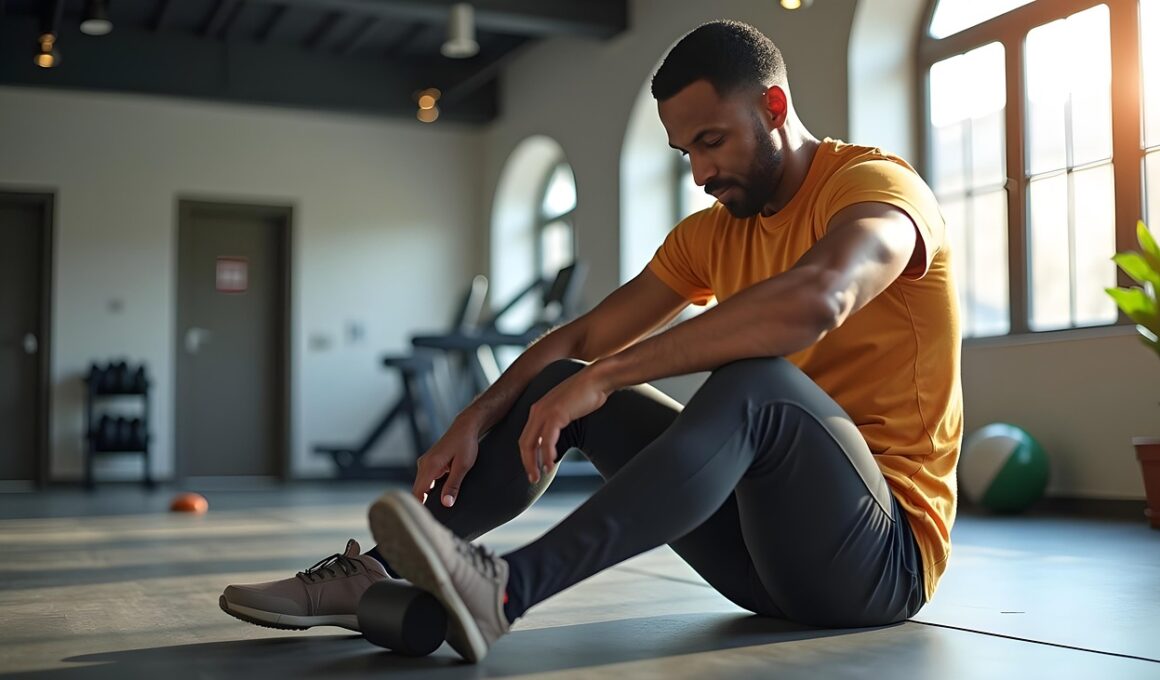
Functional training focuses on exercises that improve everyday movements, benefiting those with arthritic joints significantly. By incorporating adaptations specific to the needs of these individuals, functional training can enhance mobility and strength while reducing pain. The main objective is to focus on exercises that mimic daily activities, which allows arthritic patients to regain independence. Exercises should be tailored to the individual’s pain levels and joint restrictions, ensuring that they do not exacerbate the condition. Resistance bands and light weights are excellent tools; they effectively enhance joint stability and improve muscle strength without excessive strain. Additionally, including flexibility and mobility exercises helps maintain joint range of motion and decrease stiffness. Consistent training can lead to improved coordination and proprioception, reducing the risk of falls and injuries. Moreover, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional or certified trainer when starting a new exercise regimen. They can provide insights into the safest and most effective practices. Incorporating rest and recovery is also crucial, allowing the body to heal while still engaging in regular physical activity. Ultimately, adapted functional training can lead to a more active and happier life for those with joint issues.
One effective strategy in functional training for joint health is the use of bodyweight exercises. These exercises minimize the stress on joints while maintaining overall fitness. An example includes wall sits, which strengthen the quadriceps without significant joint impact. Another beneficial exercise is the bridge, targeting the glutes and hamstrings and enhancing core stability. These movements engage multiple muscle groups, promoting better overall functionality. Standing exercises that incorporate balance can also be beneficial, such as single-leg stands or using a balance board. This adds an element of proprioception that is vital in preventing falls, especially for older adults with arthritis. It’s essential to ensure proper form is maintained during all exercises to prevent undue stress on the joints. Gradually increasing intensity and duration allows for optimal strength gains while minimizing discomfort. Incorporating low-impact cardio, such as walking or cycling, alongside strength training will further improve joint function and cardiovascular health. Always remember to warm up before training and cool down afterward to reduce joint stiffness. Additionally, water-based exercises can provide a supportive environment for arthritic joints, allowing for a greater range of motion with less pain.
Importance of Mobility and Flexibility
Mobility and flexibility training play crucial roles in maintaining joint health for individuals with arthritis. Incorporating dynamic stretches targeting the affected joints before physical activities is vital for warming up. These stretches prepare the muscles and joints for movement, reducing the risk of injury. Examples include arm circles or leg swings that promote blood flow and increase overall elasticity. After training, static stretching should also be integrated, focusing on lengthening the muscles and improving joint range of motion. Gentle yoga routines can be particularly advantageous, offering both flexibility and strength enhancements through slow, controlled movements. Practicing yoga under guidance ensures that individuals with arthritis can safely target necessary muscle groups without overexerting themselves. Breathing techniques often incorporated into yoga can further reduce stress and enhance relaxation, which is beneficial because stress can exacerbate pain levels in arthritic joints. Focusing on postural alignment during exercises also protects joints from unnecessary strain. Moreover, incorporating foam rolling after workouts can improve muscle elasticity and alleviate tension. Ultimately, integrating mobility and flexibility into one’s training regimen fosters better joint health and overall well-being for people with arthritis.
Another essential element of functional training for arthritic joints involves strength training tailored to the individual’s needs. Research indicates that strengthening the surrounding muscles can enhance joint stability, reducing pain during daily activities. Resistance exercises can be performed using lightweight dumbbells, resistance bands, or even bodyweight. Targeting specific muscle groups, such as the quadriceps, hamstrings, and core muscles, can significantly impact overall functional ability. Exercises like squats and lunges, modified as needed, serve to support excellent mobility and core strength. Consider introducing multi-joint exercises that simulate everyday movements; they assist in building functional strength efficiently. Gradually increasing resistance or complexity ensures progression without risking injury. Inclusion of core exercises, such as planks and seated twists, further strengthens the muscles that support the spine, contributing to posture enhancement and pain reduction. Working with a certified trainer or physical therapist provides valuable insights and ensures proper form and technique, which are paramount for arthritic patients. Adapting workouts based on daily variations in pain levels is essential while maintaining consistency in overall training. Clear monitoring of progress contributes to motivation and a tangible sense of achievement, fostering long-term adherence to the fitness program.
Dietary Considerations for Joint Health
Diet plays a vital role in supporting joint health and can complement functional training for arthritic individuals. Consuming an anti-inflammatory diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help manage arthritis symptoms. Foods such as fatty fish like salmon, walnuts, and flaxseeds contain omega-3 fatty acids, which are known for their anti-inflammatory properties. Additionally, incorporating colorful fruits and vegetables provides antioxidants that combat oxidative stress responsible for joint inflammation. Staying properly hydrated is equally important, as it supports overall cellular function and joint lubrication. Reducing processed foods and sugar intake can also alleviate exacerbations of arthritis symptoms. Those with joint issues should consider monitoring their diet to identify any specific food triggers that worsen inflammation. A balanced diet contributes to weight maintenance, minimizing unnecessary stress on already compromised joints. Consulting with a healthcare professional or nutritionist ensures that dietary strategies align with individual health requirements. Incorporating mindful eating practices further enhances the relationship with food, promoting overall wellness alongside functional training. Ultimately, combining appropriate dietary practices with functional exercises leads to significant improvements in joint health and overall quality of life.
Monitoring progress is crucial for individuals participating in functional training tailored for arthritic joints. Keeping track of improvements in mobility, strength, and pain levels helps individuals understand what works best for them. This can be achieved through journaling, noting daily exercises completed, and any significant physical changes noticed. Setting attainable short-term and long-term goals fosters a sense of accomplishment and motivation. Checking in with a healthcare professional periodically allows for guidance on adjusting workout plans if needed, ensuring safety and efficiency. Regular assessments can indicate necessary modifications to exercises based on current levels of capability or pain. Utilizing technology can further aid in tracking progress; fitness apps or activity trackers can provide a comprehensive overview of daily physical activity. Furthermore, creating a support network with fellow participants or health professionals encourages shared experiences, motivation, and accountability. Sharing victories, challenges, and tips with each other can significantly enhance commitment to training regimes. It’s essential also to celebrate small achievements, no matter how minor they may seem, as they contribute to gradual improvements in one’s health journey. Overall, continuous evaluation and support will enhance adherence to functional training, ultimately leading to better joint health.
The Role of Professional Guidance
Seeking professional guidance is imperative for individuals embarking on functional training for joint health. Collaborating with a certified personal trainer or physical therapist experienced in joint health issues ensures a personalized approach tailored to one’s unique needs. These experts can facilitate an accurate assessment of physical capabilities and limitations, guiding participants through appropriate exercises. Furthermore, they can demonstrate correct techniques, helping to prevent injuries and maximize benefits. Regular sessions with professionals provide accountability, motivation, and structure to the training regimen. It is also essential to communicate any discomfort or changes in symptoms continuously, as these insights inform program adjustments. Attending classes focused on functional training, designed for individuals with joint issues, offers supportive environments that foster community and shared experiences. Such settings encourage participants to stay committed to their health goals while learning valuable movement strategies. Additionally, professionals can provide educational resources regarding joint health, proactive management, and self-care strategies. Ultimately, the combination of functional training with professional guidance empowers individuals to reclaim their activity levels while enhancing joint stability and overall quality of life.