Physical Therapy Protocols for Stress Fracture Healing
Stress fractures often occur due to repetitive activities or excessive loads on the bones, leading to small cracks in the bone structure. Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the recovery process, helping patients regain strength and mobility. The initial approach typically involves reducing weight-bearing activities to allow for healing. Providing a supportive environment is vital for recovery. A therapist will evaluate the specific stress fracture location, assessing the severity and creating an individualized treatment plan. Gentle range-of-motion exercises can help maintain joint flexibility. Incorporating strengthening exercises is essential for rebuilding muscle around the affected area while preventing future injuries. Balance training can also be integrated to improve stability and coordination. Gradual increase in the intensity of exercises helps to prevent re-injury. Utilizing modalities such as ultrasound or electrical stimulation can assist in pain management and soft tissue healing. Education on proper footwear and biomechanics during activities is crucial for long-term recovery. This comprehensive approach ensures that the patient is not only healing effectively but also minimizing the risk of future stress fractures upon returning to sport or physical activity.
Once the acute pain and inflammation have subsided, progressive loading becomes an essential part of the rehabilitation protocol for stress fractures. This phase focuses on gradually reintroducing weight-bearing activities under professional supervision. Physical therapists will design a tailored program that combines low-impact activities with functional movements. This structured approach allows patients to adapt their muscles and bones to increased stress safely. Exercises that focus on strengthening the surrounding musculature are prioritized. Exercises such as calf raises, leg presses, and resistance band workouts are commonly used for this purpose. It is crucial to maintain open communication with the therapist during this phase. Reporting any discomfort or pain immediately helps to adjust the program accordingly. Cardio-training options like cycling or swimming are valuable alternatives, allowing patients to maintain fitness without overstressing the healing bone. Additionally, the therapist may incorporate jumping exercises as patients progress. It is important to gradually increase intensity while monitoring the response. This phase may last several weeks, depending on the individual’s healing rate. Such meticulous attention ensures that patients return to full activity levels safely and effectively.
Importance of Gait Training
As patients transition back to full weight-bearing activities, gait training becomes essential in the physical therapy protocols for stress fracture recovery. Gait analysis by a physical therapist helps identify abnormalities in walking patterns that may contribute to further injuries. Furthermore, correcting these patterns ensures the efficient use of energy and minimizes strain on the recovering bone. A combination of manual therapy and tailored exercises assists in facilitating proper body mechanics during ambulation. Focused training may include treadmill sessions, overground walking programs, or balance drills on unstable surfaces. Implementing visual feedback through video analysis can further enhance a patient’s awareness of their gait. Emphasizing synchronization between lower body movements aids in developing a more natural and efficient walking pattern. The therapist may also introduce agility drills once the patient is stable. Additionally, education about footwear and surface selection remains paramount. Wearing appropriate supportive shoes minimizes the risk of reinjuring the stress fracture. Regular follow-up appointments assess progress and ensure that the transitions to more dynamic activities align with the patient’s evolving capabilities. Therefore, addressing all gait-related concerns is integral for optimal healing and performance.
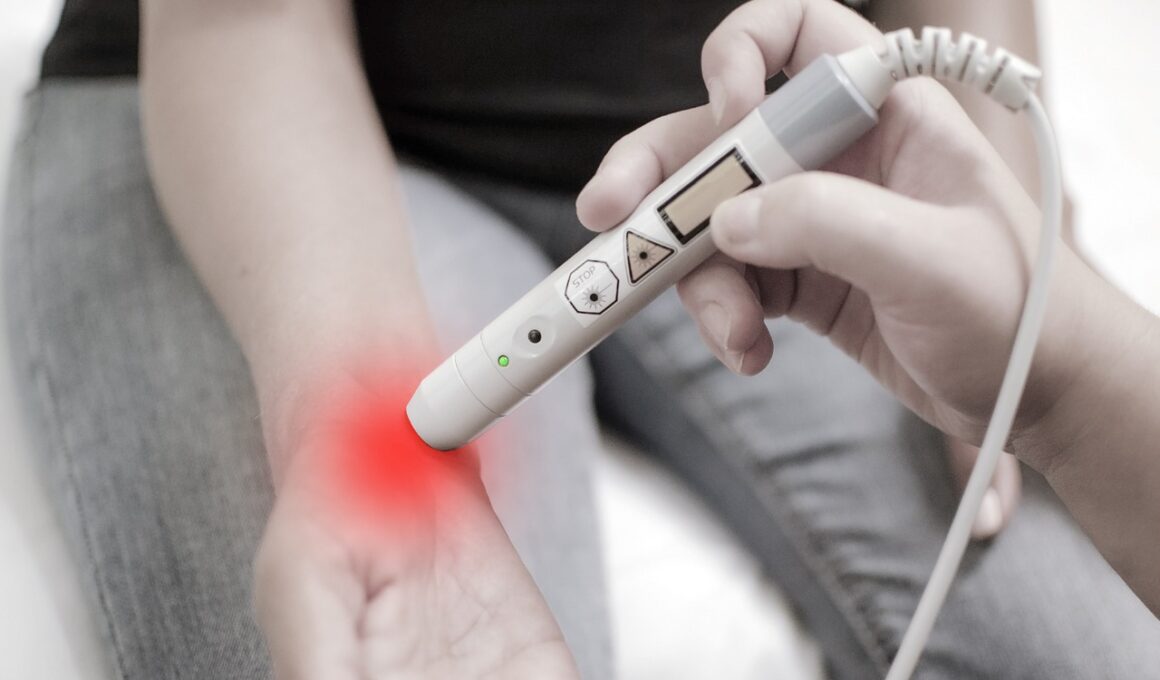
Another critical component of the treatment protocol involves therapeutic modalities that enhance healing and relieve pain. Modalities used in physical therapy include ultrasound, cryotherapy, and electrical stimulation. These techniques can help manage discomfort and promote quicker recovery during the rehabilitation process. Ultrasound therapy, for instance, utilizes sound waves to accelerate tissue healing and reduce inflammation. Implementing cold therapies, such as ice packs or cold compression devices, can alleviate pain and swelling in the early stages. Meanwhile, electrical stimulation can promote muscle contractions, enhancing the strength of surrounding support structures. Often, a combination of these modalities is recommended. Understanding the patient’s pain threshold is crucial; therefore, customizing treatment plans according to individual responses is essential. Additionally, physical therapists will regularly assess the effectiveness of the modalities. Proper training on how to utilize these therapies will empower the patient to continue managing their symptoms independently at home. Incorporating self-management techniques not only aids in physical healing but also contributes positively to mental well-being. This holistic approach builds patient confidence and fosters a proactive attitude toward recovery, ensuring patients engage fully in their rehabilitation journey.
Enhancing Nutritional Support
Nutrition also plays a pivotal role in supporting recovery from stress fractures. Adequate nutrition helps in ensuring optimal bone health and enhances healing. Physical therapists often work in conjunction with nutritionists to develop dietary plans that promote recovery. Key nutrients such as calcium and vitamin D are crucial for bone strength and repair. Consuming foods rich in these nutrients, like dairy products, leafy greens, and fish, is encouraged. Additionally, protein intake is vital since it supports muscle rejuvenation and repair. Foods such as lean meats, legumes, and nuts should be included in daily meals. Hydration also significantly contributes to overall health and recovery. Drinking sufficient water aids in nutrient absorption and promotes cellular functions. A balanced diet, tailored by professionals, ensures patients meet their individual physiological requirements. Moreover, educating patients about the importance of nutrition can empower them to take control of their recovery process. Nutrition guidelines should be practical, focusing on realistic meal planning and cooking methods. Patients often benefit from continuous support and accountability in their nutritional choices, further enhancing their journey towards optimal recovery from stress fractures.
Finally, psychological aspects should not be overlooked during rehabilitation from stress fractures. Adapting to physical limitations and lifestyle changes can cause psychological stress. Incorporating mental health support within physical therapy protocols becomes essential for overall recovery. Physical therapists can address patients’ emotional and psychological needs by using motivational interviewing techniques. These techniques help raise awareness of any anxiety experienced during the rehabilitation process. Additionally, establishing achievable goals can foster a sense of accomplishment and motivate patients to adhere to their treatment plans. Regular check-ins regarding emotional well-being can facilitate open discussions about stress and coping strategies. Many therapists might also work alongside psychologists specializing in sports rehabilitation. Group therapy sessions can create a supportive environment where individuals share their experiences and learn from one another. Incorporating mindfulness techniques can assist in stress relief and focus during therapy sessions. This overall integrative approach encourages resilient coping mechanisms, allowing patients to manage their rehabilitation journey confidently. Emphasizing mental health not only supports physical healing but also empowers patients to return to their desired activities with a renewed sense of strength and purpose.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, following a comprehensive and structured physical therapy protocol is vital for successful stress fracture healing. By focusing on a multi-faceted approach, including progressive loading, gait training, and therapeutic modalities, patients are well-equipped for recovery. Nutrition and mental health support further enhance the healing process, ensuring that patients can regain their strength effectively and efficiently. Ongoing research continues to explore the newest treatment techniques and interventions. Keeping abreast of these developments enables therapists to provide evidence-based care tailored to each patient’s needs. Innovative approaches, like virtual reality for rehabilitation, are emerging, capturing interest among professionals in physical therapy. As our understanding of stress fractures improves, so does our ability to effectively manage and prevent injuries. Emphasizing patient education throughout therapy empowers individuals and fosters autonomy, which translates to better long-term outcomes. Ultimately, combining medical treatment with therapeutic exercise, nutrition, and emotional support enables patients to return to their daily lives confidently and actively. With the right protocols in place, stress fractures can heal effectively, paving the way for a healthier, injury-free future.
Thank you for exploring physical therapy protocols for stress fracture healing! Your health journey is significant. The options discussed in this article highlight the importance of multi-dimensional care. Please consult with your healthcare professional to derive a personalized recovery plan tailored to your needs. This collaboration ensures that you are following appropriate treatment for your specific condition.